Gas Detector Tubes
Gas detectorii tubi / Gas detector tubes
Gas detector tubes are cylindrical, sealed tubes constructed from an inert transparent material and designed to allow passage of a gas sample. They contain reagents adsorbed onto inert substrates that visualise the target substance. Where necessary, preliminary layers and/or adsorbent filters are included to eliminate interfering substances. The indicator layer may contain a single reagent for detection of a specific impurity (monolayer tube) or several reagents to detect multiple substances (multilayer tube). This section describes principle, operating conditions, typical detector tube types and performance criteria used in the European Pharmacopoeia context.
Principle
The test is performed by passing a defined volume of the gas to be examined through the indicator tube. A chemical reaction between the target analyte and the reagent(s) causes the formation of a coloured layer or a colour change along the tube. The length of the coloured layer or the intensity of the colour on a graduated scale provides an indication of the concentration of the impurity present. Calibration of detector tubes shall be verified and maintained according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Characters
Construction: Cylindrical, sealed tube made of inert, transparent material with reagent(s) immobilised on an inert substrate.
Indicator layer: Monolayer (single reagent) or multilayer (multiple reagents) depending on the intended analyte(s).
Filters and preliminary layers: Adsorbent filters or preliminary reaction layers may be present to remove interfering compounds prior to the indicator layer.
Readout: Visual readout by measuring coloured layer length on a graduated scale or by comparing colour intensity to a reference scale.
Range and sensitivity: Manufacturer-specified minimum detectable value and relative standard deviation (RSD) for each tube type; see examples below.
Identification
- Tube type and code: Confirm tube identity against manufacturer labelling and leaflet (tube code, lot number, expiry date).
- Reagent system: Verify the reagent(s) listed in the leaflet correspond to the intended analyte.
- Visual inspection: Ensure tube integrity (no cracks, proper seals) and absence of discoloration or moisture prior to use.
Calibration and Verification
Calibration of detector tubes shall be verified in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions. Where applicable, verification may be performed using certified calibration gases or reference atmospheres containing the relevant impurity at a known concentration. If negative or unexpected results are obtained, tubes should be checked against calibration gas or replaced. For compressor oil detection, verify tube reactivity specifically for the oil used—consult the manufacturer's reactivity leaflet or request manufacturer validation when the oil is not listed.
Operating Conditions
Examine according to the manufacturer's instructions or proceed as follows:
- Connect the gas supply to a suitable pressure regulator and a needle valve to control flow.
- Attach flexible tubing fitted with a Y-piece to the needle valve and adjust flow to purge the tubing until a steady, appropriate flow is established (see Figure 2.1.6.-1).
- Prepare the indicator tube and fit it to the metering pump as instructed by the tube manufacturer.
- Connect the open end of the indicator tube to the short leg of the Y-piece tubing.
- Operate the indicator tube pump by the number of strokes required to pass the specified volume of gas through the tube (manufacturer-specified strokes or volume).
- Read the result by measuring the length of the coloured layer or assessing the colour intensity against the graduated scale on the tube.
If a negative result is obtained but the presence of the analyte is suspected, verify tube response using an appropriate calibration gas containing the impurity at a known concentration. Maintain environmental and flow conditions within ranges recommended by the tube manufacturer to avoid bias.
Apparatus
The apparatus typically comprises the following elements
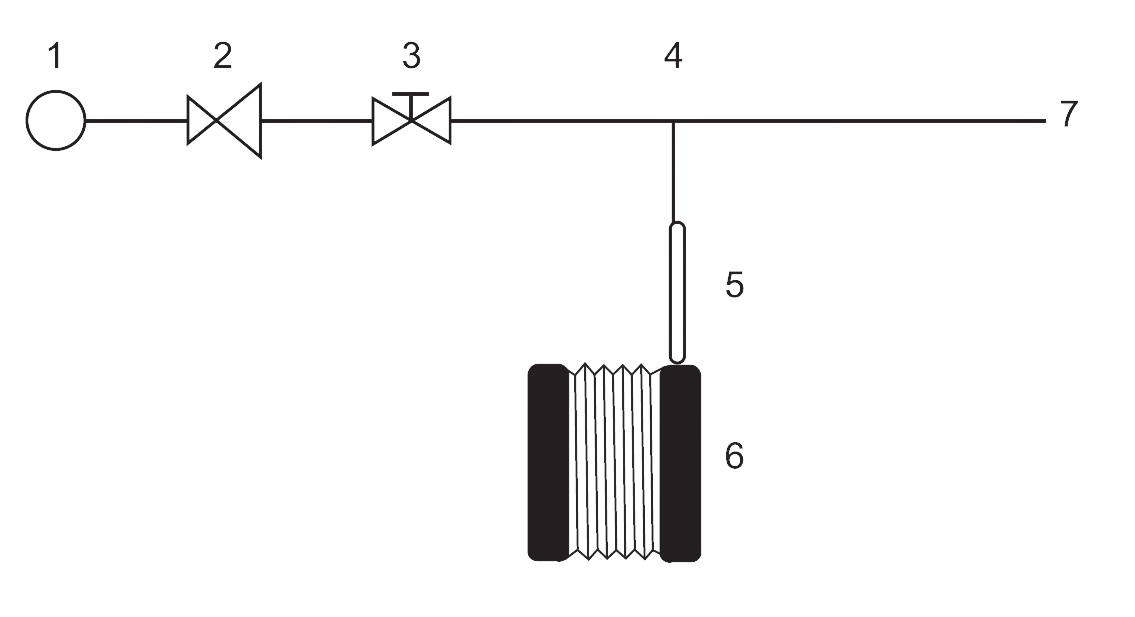
- Gas supply
- Pressure regulator
- Needle valve
- Y-piece
- Indicator tube
- Indicator tube pump (metering pump)
- End open to atmosphere
Examples of Detector Tubes and Performance Criteria
- Arsine detector tube: Sealed glass tube containing adsorbent filters and supports for gold salt or equivalent indicator. Minimum indicated value: 0.25 ppm or less; relative standard deviation (RSD) ≤ 20%.
- Carbon dioxide detector tube: Sealed glass tube with adsorbent filters and supports for hydrazine and crystal violet indicators. Minimum indicated value: 100 ppm; RSD ≤ 15%.
- Carbon monoxide detector tube: Sealed glass tube with adsorbent filters and supports for di-iodine pentoxide, selenium dioxide and fuming sulfuric acid indicators. Minimum indicated value: 5 ppm or less; RSD ≤ 15%.
- Hydrogen sulfide detector tube: Sealed glass tube with adsorbent filters and supports for an appropriate lead salt indicator. Minimum indicated value: 0.2 ppm or less; RSD ≤ 10%.
- Nitrogen monoxide / nitrogen dioxide detector tube: Sealed glass tube with adsorbent filters and supports for an oxidising layer (Cr(VI) salt) and diphenylbenzidine indicator. Minimum indicated value: 0.5 ppm; RSD ≤ 15%.
- Oil detector tube: Sealed glass tube with adsorbent filters and supports for a sulphuric acid indicator. Minimum indicated value: 0.1 mg/m³; RSD ≤ 30%. (Reactivity must be confirmed for specific compressor oils.)
- Phosphine detector tube: Sealed glass tube with adsorbent filters and supports for gold salt or equivalent indicator. Minimum indicated value: 0.2 ppm or less; RSD ≤ 20%.
- Sulfur dioxide detector tube: Sealed glass tube with adsorbent filters and supports for iodine and starch indicator. Minimum indicated value: 0.5 ppm; RSD ≤ 15%.
- Water vapour detector tube: Sealed glass tube with adsorbent filters and supports for magnesium perchlorate indicator. Minimum indicated value: 67 ppm or less; RSD ≤ 20%.
Performance and Quality Requirements
For each detector tube type, manufacturers shall provide performance data including the minimum detectable concentration (limit of detection), the relative standard deviation (precision) at representative concentrations, linearity range, recommended sample volumes or pump strokes, and any known interferences. Tubes shall conform to stated performance characteristics when stored and used according to the manufacturer's instructions. Users should ensure lot-specific validation or verification when required by local quality systems.
Interferences and Precautions
- Certain compounds may cause false positives or negatives by reacting with reagent layers or by masking the analyte; manufacturers typically list common interferences in the tube leaflet.
- Adsorbent filters and preliminary layers are intended to reduce such interferences but may not remove all interfering species.
- Environmental factors (temperature, humidity, pressure) and flow rate deviations can affect the accuracy of readings; follow manufacturer-specified operating ranges.
- Handle tubes as fragile sealed glassware; avoid exposure to moisture prior to use and do not reuse single-use tubes.
Reporting and Interpretation
Report results as the concentration indicated by the length of the coloured layer or as described by the manufacturer's calibration curve. When reporting, include tube type and code, lot number, number of pump strokes (or volume), ambient conditions (temperature, relative humidity), and whether a calibration or verification gas was used. Where required by regulatory or quality systems, confirm positive or critical results using a reference analytical method (e.g., instrument-based gas analysis) or by cross-check with a certified calibration gas.
